Saturday, December 5, 2009
Steve JObs On Firing
"We’ve had one of these before, when the dot-com bubble burst. What I told our company was that we were just going to invest our way through the downturn, that we weren’t going to lay off people, that we’d taken a tremendous amount of effort to get them into Apple in the first place – the last thing we were going to do is lay them off."
This Just shows, that the CEO of the most chic organization knows how to take care of his subordinates, and this thing certainly keeps the workers more focused, enthusiastic and going.
Plus, this quote of his also explains, why Apple has always got out of every difficult situation !! Instead of focusing on firing the workforce and other such unnecessary tactics, Apple has always stayed focused on fighting the circumstances
And that's a food for thought for those of us who manage to get a top position in some organization !
Steve Jobs On Hiring
So, in the end, it’s ultimately based on your gut. How do I feel about this person? What are they like when they’re challenged? I ask everybody that: ‘Why are you here?’ The answers themselves are not what you’re looking for. It’s the meta-data."
Well, here Steve Jobs has expresses his views about Hiring people, which is definitely a crucial part of an organization's strategy.
As you see over here, he has confessed hiring people just on objective analysis can prove tricky and in the long run one has to consider his gut feeling. But even for that you have to analyze the person in question thoroughly. YOu have to consider what the person is like and you also have to see how he/she will fit into your organization at various times i.e, during challenges, everyday etc.
And in the end, it's ultimately based on your get and what kind of vibes you get
Only 3 Importent Sentences
1- Customer directs ur business.
2- Customer Grows ur business.
3- Customer Improves ur business.
It shows that customers Shapes ur business. In my openion every business is all about the care of ur customers.. If ur customers are not satisfied then ur business is all it vain.. Because if u dont have customers to sell ur products then there is no purpose of carrying a business. Because ur products will remain unuseful.. The same thing PTCL is doing that earleir dail up connections were only capable of using internet. but ur telephone remain bussy. By that prblem, the customers were moving towards their local area wired internet..Then by taking feedbacks from their customers thay designed broadband in which customers can use internet as well as phone calls. This thing give PTCL a new business in shape of Broadband Internet.. SO customers plays a vital role in shaping and growing ur business,,,,that what PTCL learned and got a new business...
Difference between value based and cost based pricing:
Value-based pricing focuses on the price we believe customers are willing to pay, based on the benefits our business offers us. Value-based pricing depends on the strength of the benefits we can prove our offer to customers. This approach can prove very profitable, it can alienate potential customers who are driven only by price and can also draw in new competitors.
Social networking are becoming part of business strategy in US.

My opinion:
A recent research shows social networking activites of US companies till april 2009. In US, social networking is becoming very popular, and a large number of companies are using it for marketing and advertising. Now in US, social networking are becoming part of business and operations strategy. 31% of CEO of US companies are on facebook, and 14% are on twitter. Now 18% companies have an employee-created facebook group.
source: emarketer.com
Make Your Business More Successful through Telemarketing.
Telemarketing is very important in every business nowadays, because it is an effective way to know the needs and wants of your customers and also a way on how to respond on them effectively. There are lots of telemarketing companies that come out now, and one of it is the Touchbusiness. Similar to other Telemarketing UK companies, Touchbusiness is known for its excellent and outstanding services providing beneficial advantages to their clients.
Marketing Yourself Online
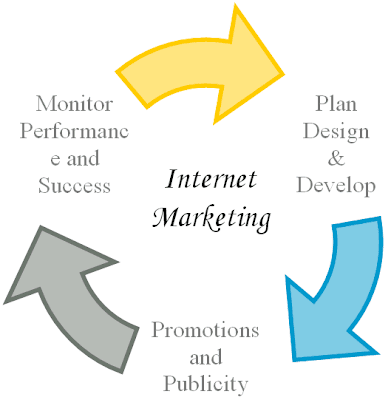
Here are few steps how to market yourself online. please check it.
The first step to marketing yourself on the Internet is deciding what it is you want to offer to people. This could be a variety of things. Once you have decided upon your niche, you must market yourself in a way that makes others want to utilize your products or services. Many people despise talking themselves up, but this is the time you must do this. For almost any idea, there are many others with the same or similar one, so you have to find methods of delivering your services in unique ways. This allows your business to stand out amongst the many others.
Online marketing is not something that happens overnight. Through your creativity and perseverance, however, you will find ways to bring some of the business right to your own doorstep, while you are also knocking on the doors where prospective business deals await.
source: http://interactiveonline.com/marketing/marketing-yourself-online
Social Media Marketing Speech Bubbles
 Social Media Marketing is really the trend these days. It is unavoidable, it is everywhere. Turn on the news and it is Twitter this and Twitter that!
Social Media Marketing is really the trend these days. It is unavoidable, it is everywhere. Turn on the news and it is Twitter this and Twitter that!image source: http://socialhoneycomb.com/social-media-marketing-speech-bubbles
salience AND sales
Last year, Hyundai did a major ZAG. Other car companies decided to play the “Zero Down. Zero % Financing.” card as well as the “Employee Discount for Everyone” card to rescue drowning sales. Hyundai didn’t. Hyundai zagged while others zigged.
Source: http://brandautopsy.typepad.com/brandautopsy/2009/03/salience-and-sales.html
SAP - An Innovate Business Software Company
-My Father
Introduction:
One of the most distinctive and striking feature of SAP, a business software provider of IT and business solutions and services, is growth by innovation. Established in 1972 by five former IBM employees – Dietmar Hopp, Hans-Werner Hector, Hasso Plattner, Klaus Tschira, and Claus Wellenreuthe by the name of S-A-P (Systems Applications and Product), it has followed only one thought pattern which has become its tradition - namely, innovation and growth. It is quite evident from the fact that in 1998 it came on the world's largest stock exchange, the New York Stock Exchange.
Clarity of Vision:
I was amazed by the clarity of its vision about its strategy, explained in depth in a very short and plain sentence, which goes as: Our vision is "to develop standard application software for real-time business processing." [1]
It is "world's leading provider of business software." It is interesting to note further is it's clarity about what business software is about. It says:
SAP defines business software as comprising enterprise resource planning and related applications such as supply chain management, customer relationship management, product life-cycle management, and supplier relationship management.
A Brief Introduction to Its Business:
Its introduces its business in these words:
SAP is the world's leading provider of business software, offering applications and services that enable companies of all sizes across more than 25 industries to become best-run businesses. With approximately 76,000 customers (including customers from the acquisition of Business Objects) in over 120 countries, the company is listed on several exchanges, including the Frankfurt stock exchange and NYSE, under the symbol "SAP."
Business and Corporate Overview (U.S. GAAP)
|
Its BusinessObject Portfolio:
SAP BusinessObject provides solutions through software, It and web-led tools and applications (real time business processing) to two kinds of enterprises and organizations:
1. Large Enterprises
2. Small and Mid-size Enterprises
Read a summary on its services and solution platforms here.
Its Industries:
SAP provides software and counsel services to a vast number of industries ranging from mining/oil and gas companies to public security and health & care institutions. Almost all kinds of service-oriented companies and industries are benefiting world-wide from its innovate IT-led solution systems.
It provides:
1. Financial and Public Services (banking, defense & security, insurance, etc)
2. Manufacturing (aerospace manufacturers, mill products, mining, oil & gas etc)
3. Service to other businesses like media, professional services, entertainment industry, distribution, travel & logistics, etc.
...................................................................................................................
For further and detailed information, please visit SAP's official website: http://www.sap.com/index.epx
Customer relationship management (CRM)
Initiatives often fail because implementation was limited to software installation, without providing the context, support and understanding for employees to learn.
Tools for customer relationship management should be implemented "only after a well-devised strategy and operational plan are put in place"
Other problems occur when failing to think of sales as the output of a process that itself needs to be studied and taken into account when planning automation.
From the outside, customers interacting with a company perceive the business as a single entity, despite often interacting with a number of employees in different roles and departments. CRM is a combination of policies, processes, and strategies implemented by an organization to unify its customer interactions and provide a means to track customer information. It involves the use of technology in attracting new and profitable customers, while forming tighter bonds with existing ones.
CRM includes many aspects which relate directly to one another:
Front office operations — Direct interaction with customers, e.g. face to face meetings, phone calls, e-mail, online services etc.
Back office operations — Operations that ultimately affect the activities of the front office (e.g., billing, maintenance, planning, marketing,advertising, finance, manufacturing, etc.)
Business relationships — Interaction with other companies and partners, such as suppliers/vendors and retail outlets/distributors, industry networks (lobbying groups, trade associations). This external network supports front and back office activities.
Analysis — Key CRM data can be analyzed in order to plan target-marketing campaigns, conceive business strategies, and judge the success of CRM activities (e.g., market share, number and types of customers, revenue, profitability).
Proponents of CRM software claim that it not only allow customer relationships to be managed more efficiently, but also encourages a more customer-centric approach to conducting business
Executives often cite the lack of proper tools as a barrier to delivering the experience their customers expect. A 2009 study of over 860 corporate executives revealed only 39% believe that their employees have the tools and authority to solve customer problems.
Friday, December 4, 2009
Marketing Product
Robert G Allen
Top 7 Sales Blunders-Avoiding sales mistake:
Sales Mistake # 1: Allowing a prospect to lead the sales process. The best way to control the sales interaction is to ask questions. This is also the best way to learn whether or not your product or service meets the needs of your prospect. Quality questions that uncover specific issues, problems, or corporate objectives are essential in helping you establish yourself as an expert.
Sales Mistake # 2: Not completing pre-meeting research. After several weeks of voice mail I finally connected with my prospect and scheduled a meeting. Unfortunately, I entered the meeting without first researching the company. Instead of presenting a solution to an existing problem, I spent the entire meeting learning fundamental information, which to senior executives, is a complete waste of their time. This approach is one of most common sales mistakes. Invest the time learning about your prospect before you call them and before you try to schedule a meeting.
Sales Mistake # 3: Talking too much. Too many sales people talk too much during the sales interaction. They espouse about their product, its features, their service and so on. When I first bought carpet for my home I recall speaking to a sales person who told me how long he had been in the business, how smart he was, how good his carpets were, etc. But this dialogue did nothing to convince me that I should buy from him. Instead, I left the store thinking that he did not care about my specific needs. A friend of mine is in the advertising business and often talks to prospects who initially request a quote. Instead of talking at great length about the ad agency’s experience and qualifications, he gets the potential client talking about her business. By doing this he is able to determine the most effective strategy for that prospect.
Sales Mistake # 4: Giving the prospect information that is irrelevant. When I worked in the corporate world I was subjected to countless presentations where the sales person shared information that was completely meaningless to me. I don’t care about your financial backing or who your clients are. Make the most of your presentation by telling me how I will benefit from your product or service until I know how your product or service relates to my specific situation.
Sales Mistake # 5: Not being prepared. I remember calling a prospect expecting to receive his voice mail. That meant I was completely unprepared when he answered the call himself. Instead of asking him a series of qualifying questions I simply responded to his questions, allowing him to control the sale. Unfortunately, I didn’t progress any further than that initial call. When you make a cold call or attend a meeting with a prospect it is critical that you are prepared. This means having all relevant information at your fingertips including; pricing, testimonials, samples, and a list of questions you need to ask. I suggest creating a checklist of the vital information you will need and reviewing this list before you make your call. You have exactly one opportunity to make a great first impression and you will not make it if you are not prepared.
Sales Mistake # 6: Neglecting to ask for the sale. I recall a participant in one of my workshops expressing interest in my book. I told him to look through it but at no time did I ask for the sale. Later, I heard him express this observation to other participants in the program. If you sell a product or service, you have the obligation to ask the customer for a commitment, particularly if you have invested time assessing their needs and know that your product or service will solve a problem. Many people are concerned with coming across as pushy but as long as you ask for the sale in a non-threatening, confident manner, people will usually respond favorably.
Sales Mistake # 7: Failing to prospect. This is one of the most common mistakes independent business make. When business is good many people stop prospecting, thinking that the flow of business will continue. However, the most successful sales people prospect all the time. They schedule prospecting time in their agenda every week.
Even the most seasoned sales professional makes mistakes from time to time. Avoid these blunders and increase the likelihood of closing the sale.
6 Sure Ways to Increase Sales:
Give your sales staff a reason to get out there and sell, sell, sell. Why do so many businesses that rely on their sales staff to drive sales have incentive programs in place? Because offering their sales staff the trips and/or TVs for x amount of sales works. See Paul Shearstone’s Creating Sales Incentive Programs That Work for how to make your sales incentive program “sweet and simple and attainable”.
2. Encourage your sales staff to upsell.
Essentially, upselling involves adding related products and/or services to your line and making it convenient and necessary for customer to buy them. Just placing more products near your usual products isn’t going to increase your sales much. To upsell successfully, the customer has to be persuaded of the benefit. For instance, when I last had my carpets cleaned, the cleaner noticed a pet stain. Instead of just cleaning it up, he drew my attention to it, and showed me how easily and effectively the spot cleaning solution removed all trace of the stain. Did I buy the spot cleaning solution? You bet. He persuaded me that buying it was beneficial to me and made it convenient to purchase it. Result: increased sales for the carpet cleaning company.
3. Give your customers the inside scoop.
Recently I was shopping at a retail housewares store. I had picked out an item and was mulling over whether to buy it or not when a salesperson came up to me and said, “I see you’re interested in that blender. We’re having a sale next week and all our blenders will be 20 percent off. You might want to come back then.” Guess what? I did – and bought two other items as well. Lesson: if you have a promotion or sale coming up, tell your customers about it. They’ll come back – and probably bring some friends with them too. (And don't forget - you can give your customers the inside scoop by emailing or calling them, too.)
4. Tier your customers.
There should be a clear and obvious difference between regular customers and other customers – a difference that your regular customers perceive as showing that you value them. How can you expect customer loyalty if all customers are treated as “someone off the street”? There are all kinds of ways that you can show your regular customers that you value them, from small things such as greeting them by name through larger benefits such as giving regulars extended credit or discounts.
5. Set up a customer rewards program.
We’re all familiar with the customer rewards programs that so many large businesses have in place. But there’s no reason that a small business can’t have a customer rewards program, too. It can be as simple as a discount on a customer’s birthday or as complex as a points system that earns various rewards such as discounts on merchandise. Done right, rewards programs can really help build customer loyalty and increase sales.
6. Distribute free samples to customers.
Why do so many businesses include free samples of other products when you buy something from them? Because it can increase sales in so many ways. As the customer who bought the original product, I might try and like the sample of the new product and buy some of it, too. Or I might pass on the sample to someone else, who might try the product, like it, and buy that and other products from the company. At the very least, the original customer will be thinking warm thoughts about your company, and hopefully telling other people about your products.
Attracting new customers is a good thing. But attracting new customers is not the only way to increase your sales, and is, in fact, the hard way of going about it. Shifting your sales focus to enticing your current customers can make increasing your sales easier – and best of all, build the customer loyalty that results in repeat sales.
Primary - Marketing Research.
Primary marketing research is collected for the first time. It is original and collected for a specific purpose, or to solve a specific problem. It is expensive, and time consuming, but is more focused than secondary research. There are many ways to conduct primary research. We consider some of them:
1. Interviews
2. Mystery shopping
3. Focus groups
4. Projective techniques
5. Product tests
6. Diaries
7. Omnibus Studies
1.0 Interviews.
This is the technique most associated with marketing research. Interviews can be telephone, face-to-face, or over the Internet.
1.1 Telephone Interview.
Telephone ownership is very common in developed countries. It is ideal for collecting data from a geographically dispersed sample. The interviews tend to be very structured and tend to lack depth. Telephone interviews are cheaper to conduct than face-to-face interviews (on a per person basis).
Advantages of telephone interviews
- Can be geographically spread
- Can be set up and conducted relatively cheaply
- Random samples can be selected
- Cheaper than face-to-face interviews
Disadvantages of telephone interviews
- Respondents can simply hang up
- Interviews tend to be a lot shorter
- Visual aids cannot be used
- Researchers cannot behavior or body language
1.2 Face-to-face Interviews.
Face-to face interviews are conducted between a market researcher and a respondent. Data is collected on a survey. Some surveys are very rigid or 'structured' and use closed questions. Data is easily compared. Other face-to-face interviews are more 'in depth,' and depend upon more open forms of questioning. The research will probe and develop points of interest.
Advantages of face-to-face interviews
- They allow more 'depth'
- Physical prompts such as products and pictures can be used
- Body language can emphasize responses
- Respondents can be 'observed' at the same time
Disadvantages of face-to-face interviews
- Interviews can be expensive
- It can take a long period of time to arrange and conduct.
- Some respondents will give biased responses when face-to-face with a researcher.
1.3 The Internet
The Internet can be used in a number of ways to collect primary data. Visitors to sites can be asked to complete electronic questionnaires. However responses will increase if an incentive is offered such as a free newsletter, or free membership. Other important data is collected when visitors sign up for membership.
Advantages of the Internet
- Relatively inexpensive
- Uses graphics and visual aids
- Random samples can be selected
- Visitors tend to be loyal to particular sites and are willing to give up time to complete the forms
Disadvantages of the Internet
- Only surveys current, not potential customers.
- Needs knowledge of software to set up questionnaires and methods of processing data
- May deter visitors from your website.
1.4 Mail Survey
In many countries, the mail survey is the most appropriate way to gather primary data. Lists are collated, or purchased, and a predesigned questionnaire is mailed to a sample of respondents. Mail surveys do not tend to generate more than a 5-10% response rate. However, a second mailing to prompt or remind respondents tends to improve response rates. Mail surveys are less popular with the advent of technologies such as the Internet and telephones, especially call centers.
2.0 Mystery Shopping
Companies will set up mystery shopping campaigns on an organizations behalf. Often used in banking, retailing, travel, cafes and restaurants, and many other customer focused organizations, mystery shoppers will enter, posing as real customers. They collect data on customer service and the customer experience. Findings are reported back to the commissioning organization. There are many issues surrounding the ethics of such an approach to research.
3.0 Focus Groups.
Focus groups are made up from a number of selected respondents based together in the same room. Highly experienced researchers work with the focus group to gather in depth qualitative feedback. Groups tend to be made up from 10 to 18 participants. Discussion, opinion, and beliefs are encouraged, and the research will probe into specific areas that are of interest to the company commissioning the research.
Advantages of focus groups
- Commissioning marketers often observe the group from behind a one-way screen
- Visual aids and tangible products can be circulated and opinions taken
- All participants and the research interact
- Areas of specific interest can be covered in greater depth
Disadvantages of focus groups
- Highly experienced researchers are needed. The are rare.
- Complex to organize
- Can be very expensive in comparison to other methods
4.0 Projective techniques.
Projective techniques are borrowed from the field of psychology. They will generate highly subjective qualitative data. There are many examples of such approaches including: Inkblot tests - look for images in a series of inkblots Cartoons - complete the 'bubbles' on a cartoon series Sentence or story completion Word association - depends on very quick (subconscious) responses to words Psychodrama - Imagine that you are a product and describe what it is like to be operated, warn, or used.
5.0 Product tests.
Product tests are often completed as part of the 'test' marketing process. Products are displayed in a mall of shopping center. Potential customers are asked to visit the store and their purchase behavior is observed. Observers will contemplate how the product is handled, how the packing is read, how much time the consumer spends with the product, and so on.
6.0 Diaries.
Diaries are used by a number of specially recruited consumers. They are asked to complete a diary that lists and records their purchasing behavior of a period of time (weeks, months, or years). It demands a substantial commitment on the part of the respondent. However, by collecting a series of diaries with a number of entries, the researcher has a reasonable picture of purchasing behavior.
7.0 Omnibus Studies.
An omnibus study is where an organisation purchases a single or a few questions on a 'hybrid' interview (either face-to-face or by telephone). The organisation will be one of many that simply want to a straightforward answer to a simple question. An omnibus survey could include questions from companies in sectors as diverse as heath care and tobacco. The research is far cheaper, and commit less time and effort than conducting your own research.
I have given a general introduction to marketing research. Marketing research is a huge topic area and has many processes, procedures, and terminologies that build upon the points above.Reference: www.marketingteacher.com
International Marketing and Culture
What is the influence of culture on international marketing?
Culture is the way that we do things around here. Culture could relate to a country (national culture), a distinct section of the community (sub-culture), or an organization (corporate culture). It is widely accepted that you are not born with a culture, and that it is learned. So, culture includes all that we have learned in relation to values and norms, customs and traditions, beliefs and religions, rituals and artefacts (i.e. tangible symbols of a culture, such as the Sydney Opera House or the Great Wall of China).
Therefore international marketing needs to take into account the local culture of the country in which you wish to market.

The Terpstra and Sarathy Cultural Framework helps marketing managers to assess the cultural nature of an international market. It is very straight-forward, and uses eight categories in its analysis. The Eight categories are Language, Religion, Values and Attitudes, Education, Social Organizations, Technology and Material Culture, Law and Politics and Aesthetics.
Language
With language one should consider whether or not the national culture is predominantly a high context culture or a low context culture (Hall and Hall 1986). The concept relates to the balance between the verbal and the non-verbal communication.
In a low context culture spoken language carries the emphasis of the communication i.e. what is said is what is meant. Examples include Australia and the Netherlands.
In a high context culture verbal communications tend not to carry a direct message i.e. what is said may not be what is meant. So with a high context culture hidden cultural meaning needs to be considered, as does body language. Examples of a high context cultures include Japan and some Arabic nations.
Religion
The nature and complexity of the different religions an international marketer could encounter is pretty diverse. The organization needs to make sure that their products and services are not offensive, unlawful or distasteful to the local nation. This includes marketing promotion and branding.
- In China in 2007 (which was the year of the pig) all advertising which included pictures of pigs was banned. This was to maintain harmony with the country's Muslim population of around 2%. The ban included pictures of sausages that contained pork, and even advertising that included an animated (cartoon) pig.
- In 2005 France's Catholic Church won a court injunction to ban a clothing advertisement (by clothing designers Marithe and Francois Girbaud) based upon Leonardo da Vinci's Christ's Last Supper.
Values and Attitudes
Values and attitudes vary between nations, and even vary within nations. So if you are planning to take a product or service overseas make sure that you have a good grasp the locality before you enter the market. This could mean altering promotional material or subtle branding messages. There may also be an issue when managing local employees. For example, in France workers tend to take vacations for the whole of August, whilst in the United States employees may only take a couple of week's vacation in an entire year.
- In 2004, China banned a Nike television commercial showing U.S. basketball star LeBron James in a battle with animated cartoon kung fu masters and two dragons, because it was argued that the ad insults Chinese national dignity.
- In 2006, Tourism Australian launched its ad campaign entitled "So where the bloody hell are you?" in Britain. The $130 million (US) campaign was banned by the British Advertising Standards Authority from the United Kingdom. The campaign featured all the standard icons of Australia such as beaches, deserts, and coral reefs, as well as traditional symbols like the Opera House and the Sydney Harbour Bridge. The commentary ran:
"We've poured you a beer and we've had the camels shampooed, we've saved you a spot on the beach. We've even got the sharks out of the pool,".
Then, from a bikini-clad blonde, come the tag line:
"So where the bloody hell are you?"
Education
The level and nature of education in each international market will vary. This may impact the type of message or even the medium that you employ. For example, in countries with low literacy levels, advertisers would avoid communications which depended upon written copy, and would favour radio advertising with an audio message or visual media such as billboards. The labelling of products may also be an issue.
- In the People's Republic of China a nationwide system of public education is in place, which includes primary schools, middle schools (lower and upper), and universities. Nine years of education is compulsory for all Chinese students.
- In Finland school attendance is compulsory between the ages of 7 and 16, the first nine years of education (primary and secondary school) are compulsory, and the pupils go to their local school. The education after primary school is divided to the vocational and academic systems, according to the old German model.
- In Uganda schooling includes 7 years of primary education, 6 years of secondary education (divided into 4 years of lower secondary and 2 years of upper secondary school), and 3 to 5 years of post-secondary education.
Social Organizations
This aspect of Terpstra and Sarathy's Cultural Framework relates to how a national society is organized. For example, what is the role of women in a society? How is the country governed - centralized or devolved? The level influence of class or casts upon a society needs to be considered. For example, India has an established caste system - and many Western countries still have an embedded class system. So social mobility could be restricted where caste and class systems are in place. Whether or not there are strong trade unions will impact upon management decisions if you employ local workers.
Technology and Material Culture
Technology is a term that includes many other elements. It includes questions such as is there energy to power our products? Is there a transport infrastructure to distribute our goods to consumers? Does the local port have large enough cranes to offload containers from ships? How quickly does innovation diffuse? Also of key importance, do consumers actually buy material goods i.e. are they materialistic?
- Trevor Baylis launched the clockwork radio upon the African market. Since batteries were expensive in Africa and power supplies in rural areas are non-existent. The clockwork radio innovation was a huge success.
- China's car market grew 25% in 2006 and it has overtaken Japan to be the second-largest car market in the world with sales of 8 million vehicles. With just six car owners per 100 people (6%), compared with 90% car ownership in the US and 80% in the UK, the potential for growth in the Chinese market is immense.
Law and Politics
As with many aspects of Terpstra and Sarathy's Cultural Framework, the underpinning social culture will drive the political and legal landscape. The political ideology on which the society is based will impact upon your decision to market there. For example, the United Kingdom has a largely market-driven, democratic society with laws based upon precedent and legislation, whilst Iran has a political and legal system based upon the teachings and principles Islam and a Sharia tradition.
Aesthetics
Aesthetics relate to your senses, and the appreciation of the artistic nature of something, including its smell, taste or ambience. For example, is something beautiful? Does it have a fashionable design? Was an advert delivered in good taste? Do you find the color, music or architecture relating to an experience pleasing? Is everything relating to branding aesthetically pleasing?
I hope this somehow acted as a bridge between culture and international marketing which needs to take into account local marketing as well.
Reference: www.marketingteacher.com
Marketing Plans
Marketing plans are vital to marketing success. They help to focus the mind of companies and marketing teams on the process of marketing i.e. what is going to be achieved and how we intend to do it. There are many approaches to marketing plans. It is contained under the popular acronym AOSTC.
ANALYSIS.
OBJECTIVES.
STRATEGIES.
TACTICS.
CONTROLS.
Stage One - Situation Analysis (and Marketing Audit).
- Marketing environment.
- Laws and regulations.
- Politics.
- The current state of technology.
- Economic conditions.
- Sociocultural aspects.
- Demand trends.
- Media availability.
- Stakeholder interests.
- Marketing plans and campaigns of competitors.
- Internal factors such as your own experience and resource availability.
Also see tools for internal/external audit:
Stage Two - Set marketing objectives.
- Specific - Be precise about what you are going to achieve.
- Measurable - Quantify you objectives.
- Achievable - Are you attempting too much?
- Realistic - Do you have the resource to make the objective happen (men, money, machines, materials, minutes)?
- Timed - State when you will achieve the objective (within a month? By February 2010?).
If you don't make your objective SMART, it will be too vague and will not be realized. Remember that the rest of the plan hinges on the objective. If it is not correct, the plan may fail.
Stage Three - Describe your target market
- Which segment? How will we target the segment? How should we position within the segment?
- Why this segment and not a different one? (This will focus the mind).
- Define the segment in terms of demographics and lifestyle. Show how you intend to 'position' your product or service within that segment. Use other tools to assist in strategic marketing decisions such as Boston Matrix , Ansoff's Matrix , Bowmans Strategy Clock, Porter's Competitive Strategies, etc.
Stage Four - Marketing Tactics.
Convert the strategy into the marketing mix (also known as the 4Ps). These are your marketing tactics.
- Price Will you cost plus, skim, match the competition or penetrate the market?
- Place Will you market direct, use agents or distributors, etc?
- Product Sold individually, as part of a bundle, in bulk, etc?
- Promotion Which media will you use? e.g sponsorship, radio advertising, sales force, point-of-sale, etc? Think of the mix elements as the ingredients of a 'cake mix'. You have eggs, milk, butter, and flour. However, if you alter the amount of each ingredient, you will influence the type of cake that you finish with.
Stage Five - Marketing Controls.
Remember that there is no planning without control. Control is vital.
- Start-up costs.
- Monthly budgets.
- Sales figure.
- Market share data.
- Consider the cycle of control.
Finally, write a short summary (or synopsis) which is placed at the front of the plan. This will help others to get acquainted with the plan without having to spend time reading it all. Place all supporting information into an appendix at the back of the plan.
This post i think takes all the marketing tools into account and gives practical application to much of the marketing strategies used.
Reference: www.marketingteacher.com
Entrepreneurship: Cure for Our Hundred Material Sorrows
***
Entrepreneurship is about starting up new business(es). The only way a new firm can make business is by delivering something that has not been offered, or, "to create products that people need but have yet not imagined." This involves a lot of 'innovation' to be done that goes beyond mere 'invention'. Hence, we have much more practical and feasible solutions for everyday problems. And, above all, entrepreneurship - like life - is about integrative thinking and action. Cross-pollination of different fields, technical and non-technical expertise goes into making innovative products and solutions for the benefit of a greater number.
The most innovative firms, like IDEO, are ones where the teams, that develop and make innovative solutions and products for real life problems, consist of people from very diverse backgrounds. IDEO, for example, was once given the task of reinventing the shopping trolley. Now imagine, you're to make a much better trolley, that is more safer, effective and efficient and cheaper, would you need biologists, marketers, psychologists, etc. to make such a product? Yes, you do in entrepreneurship to make breakthrough, cheap and efficient products.
What would be better than integration of different parts of knowledge, in our world so ruthlessly compartmentalized? With this integrative approach towards making use of knowledge, and knowing a process to innovate better products (that is Design Thinking, click to know what it is), would lead us to eliminate poverty, save energy, and make practical things that solve everyday problems. To end this post by giving a little example of how entrepreneurship, the art and science of doing business, is helping poor countries prosper and save their resources, I just need to mention about the 100 Dollar Laptop Project; One Laptop for Every Child, which is backed by world's major transnational corporations:
"Mission Statement: To create educational opportunities for the world's poorest children by providing each child with a rugged, low-cost, low-power, connected laptop with content and software designed for collaborative, joyful, self-empowered learning. When children have access to this type of tool they get engaged in their own education. They learn, share, create, and collaborate. They become connected to each other, to the world and to a brighter future."
Read more about the project, its vision and technical aspects (hardware and software), here.
Ryanair Marketing Mix.
Its charismatic boss Michael O'Leary has a business model with a central focus on cost reduction (and making money of course!). In around 20 years he has taken Ryanair from a single plane company to become the largest airline in Europe. He had a vision and achieved it through masterful leadership. So how did he do it? How does Michael O'Leary retain his narrow cost focus niche strategy in the face of intense competition? The business simply has lower costs and those costs are passed on to their passengers in the form of low fares.
The branded airlines argue that passengers are willing to pay more for a better level of service. You can pre-assign seats. You get food and drink onboard, and can choose a higher level of service e.g. business class. However the large flag carriers have taken notice of the low-cost model and have employed it as part of their own more differentiated business model.
In 2009 the company settled for 30% of its local Irish rival Aer Lingus after a prolonged takeover bid. Tough trading conditions meant that Ryanair made its first annual loss in 2008/9. O'Leary put this down firmly to rising fuel costs (as did British Airways in the same year). The company also needed to take into account the burden of purchasing its stake in Air Lingus. So in reality things are looking good for Ryanair and its budget operation - since the business aimed to fly double the amount of passengers 2009/10.
Let's take a closer look at Ryanair's marketing mix:
Product or Service.
- Low cost, no frills air travel to European destinations.
- There is no free food or drink onboard. Food and drink are income streams. You buy them onboard, or you don't - take your own food and drink if you like.
- There are other income streams - or ancillary revenue. The company has deals with Hertz car rental, and a number of hotel businesses. So Ryanair takes a commission on 'up selling' i.e. ancillary revenue. Other examples include phone cards and bus tickets. About 16% of profit is made this way. This keeps costs lower.
Price
- Ryanair has low fares.
- 70% of seats are sold at the lowest two fares.30% of seats are charged at higher fares. The last 6% are sold at the highest fare
- Ryanair occasionally get in trouble with bodies such as the Advertising Standards Authority (ASA) in the UK over differences between advertised and actual price - in fairness to Ryanair these are rare mistakes.
Place
- Ryanair does not use travel agents so it does not pay agency commissions. It uses direct marketing techniques to recruit and retain customers, and to extend products and services to them (i.e. Customer Relationship Management). This reduces costs.
- You book online over the Internet. This saves them 15% on agency fees.
- They are based in Stanstead in Essex - which is known as a secondary airport. It is new and accessible. It is cheaper to fly from Stanstead than either Heathrow or Gatwick, and since it is less busy Ryanair can turn aircraft around more quickly.
- Many of Ryanair's destination airports are secondary. For example if you fly to Copenhagen (Denmark) you arrive in Malmo (Sweden) - although it is only a short coach trip over the border. Secondary airports, which tend to be smaller regional airports, depend upon this single carrier - some (it is rumored) paying up to £100, 000 for each additional new route. Costs are lower and aircraft can be turned around faster.
- Keeping aircraft in the air as much as possible is another important part of the low cost jigsaw. However, the company has been challenged by the European Union in relation to anti-competition laws.
Promotion
- They spend as little as possible on advertising.
- They do not employ an advertising agency. Instead all of the advertising is done in-house. In fact O'Leary himself overseas much of the promotion of Ryanair. They use simple adverts that tell passengers that Ryanair has low fares.
- Ryanair employs controversy to promote its business. For example in 2009, the company reasoned that passengers would be charged £1 to use the toilets on board. O'Leary reasoned that passengers could use the terminals at either the destination or arrival airport. This would speed things up. It was reasoned that this is what passengers wanted - since they did not want other passengers leaving their seats and walking the aisles to go to the toilet. O'Leary also argued that larger passengers should be charged more since they took up more room - again it was reasoned that this is what the majority of passengers wanted.
- Some of their aircraft are decorated in the livery of advertisers e.g. News of the World, Jaguar and Kilkenny (beer).
People
- Pilots are recruited when they are young as pilot cadets. They work hard and take early promotions and then move on after 10-years or so to further their careers.
- Cabin crew pay for their uniforms to be cleaned. They invest in their own training. They are mainly responsible for passenger safety as well as ancillary revenues onboard.
Physical Evidence
- They pay as little as possible for their aircraft. Planes are the most expensive asset that an airline can make. They get big discounts on aircraft because they buy them when other airlines don't want them, for example after September 11th, or on the invasion of Iraq and Afghanistan. Aircraft manufacturers cannot simply stop a supply chain in minutes. If orders are being cancelled or delayed, this is when to buy. It was rumored within the industry that Ryanair was buying Boeing 737s - list price around £40,000,000 (forty million pounds) - with up to a 50% discount.
Process
- There is no check in. You simply show your passport and supply your reference number.
- You cannot select a preferred seat. It is first come, first served. This aids speed.
- There are no air bridges (the tunnel that connects to the side of the aircraft when to board it). You walk or are bused to the aircraft.
- Baggage is deposited directly onto the terminal - it's quick. However if your bag is broken don't expect high levels of customer service.
Beyond any doubt, Ryanair is one of the strategic marketing successes of the last decade. Undoubtedly synergized by Michael O'Leary - the low cost strategy that it employs is remarkable and industry changing. In many ways the business has looked closely at all aspects of it markets and operations to remold the industry and customer expectations in a unique way. This is how Ryanair has applied the marketing mix.
The purpose here in this post was to introduce a company and its various strategies for long run business success. Much of these marketing strategies illustrated are very much applicable to our own mangerial plans as well.
Reference: www.marketingteacher.com
Process and Services Marketing.
Process as part of the marketing mix.
Process is another element of the extended marketing mix, or 7P's.There are a number of perceptions of the concept of process within the business and marketing literature. Some see processes as a means to achieve an outcome, for example - to achieve a 30% market share a company implements a marketing planning process.
Another view is that marketing has a number of processes that integrate together to create an overall marketing process, for example - telemarketing and Internet marketing can be integrated. A further view is that marketing processes are used to control the marketing mix, i.e. processes that measure the achievement marketing objectives. All views are understandable, but not particularly customer focused.
For the purposes of the marketing mix, process is an element of service that sees the customer experiencing an organisation's offering. It's best viewed as something that your customer participates in at different points in time. Here are some examples to help your build a picture of marketing process, from the customer's point of view.
Going on a cruise - from the moment that you arrive at the dockside, you are greeted; your baggage is taken to your room. You have two weeks of services from restaurants and evening entertainment, to casinos and shopping. Finally, you arrive at your destination, and your baggage is delivered to you. This is a highly focused marketing process.
Booking a flight on the Internet - the process begins with you visiting an airline's website. You enter details of your flights and book them. Your ticket/booking reference arrive by e-mail or post. You catch your flight on time, and arrive refreshed at your destination. This is all part of the marketing process.
At each stage of the process, markets:
- Deliver value through all elements of the marketing mix. Process, physical evidence and people enhance services.
- Feedback can be taken and the mix can be altered.
- Customers are retained, and other serves or products are extended and marked to them.
- The process itself can be tailored to the needs of different individuals, experiencing a similar service at the same time.
Marketing Mix is a set of controllable tactical marketing tools that a company blends to produce the response it wants in the target market and this whole works as a compact process for long run survival and growth.
Reference: www.marketingteacher.com
SWOT Analysis Bharti Airtel
Strengths
- Bharti Airtel has more than 65 million customers (July 2008). It is the largest cellular provider in India, and also supplies broadband and telephone services - as well as many other telecommunications services to both domestic and corporate customers.
- Other stakeholders in Bharti Airtel include Sony-Ericsson, Nokia - and Sing Tel, with whom they hold a strategic alliance. This means that the business has access to knowledge and technology from other parts of the telecommunications world.
- The company has covered the entire Indian nation with its network. This has underpinned its large and rising customer base.
Weaknesses
- An often cited original weakness is that when the business was started by Sunil Bharti Mittal over 15 years ago, the business has little knowledge and experience of how a cellular telephone system actually worked. So the start-up business had to outsource to industry experts in the field.
- Until recently Airtel did not own its own towers, which was a particular strength of some of its competitors such as Hutchison Essar. Towers are important if your company wishes to provide wide coverage nationally.
- The fact that the Airtel has not pulled off a deal with South Africa's MTN could signal the lack of any real emerging market investment opportunity for the business once the Indian market has become mature.
Opportunities
- The company possesses a customized version of the Google search engine which will enhance broadband services to customers. The tie-up with Google can only enhance the Airtel brand, and also provides advertising opportunities in Indian for Google.
- Global telecommunications and new technology brands see Airtel as a key strategic player in the Indian market. The new iPhone will be launched in India via an Airtel distributorship. Another strategic partnership is held with BlackBerry Wireless Solutions.
- Despite being forced to outsource much of its technical operations in the early days, this allowed Airtel to work from its own blank sheet of paper, and to question industry approaches and practices - for example replacing the Revenue-Per-Customer model with a Revenue-Per-Minute model which is better suited to India, as the company moved into small and remote villages and towns.
- The company is investing in its operation in 120,000 to 160,000 small villages every year. It sees that less well-off consumers may only be able to afford a few tens of Rupees per call, and also so that the business benefits are scalable - using its 'Matchbox' strategy.
- Bharti Airtel is embarking on another joint venture with Vodafone Essar and Idea Cellular to create a new independent tower company called Indus Towers. This new business will control more than 60% of India's network towers. IPTV is another potential new service that could underpin the company's long-term strategy.
Threats
- Airtel and Vodafone seem to be having an on/off relationship. Vodafone which owned a 5.6% stake in the Airtel business sold it back to Airtel, and instead invested in its rival Hutchison Essar. Knowledge and technology previously available to Airtel now moves into the hands of one of its competitors.
- The quickly changing pace of the global telecommunications industry could tempt Airtel to go along the acquisition trail which may make it vulnerable if the world goes into recession. Perhaps this was an impact upon the decision not to proceed with talks about the potential purchase of South Africa's MTN in May 2008. This opened the door for talks between Reliance Communication's Anil Ambani and MTN, allowing a competing Inidan industrialist to invest in the new emerging African telecommunications market.
- Bharti Airtel could also be the target for the takeover vision of other global telecommunications players that wish to move into the Indian market.
Reference: www.marketingteacher.com
'How to Quit Your Job and Start a Company'
What is your business idea?
Can't blame mobiles anymore for brain cancer; Business opportunities
 Well, nobody has been blaming mobiles, but you can't deny that rumors are very 'sticky'.
Well, nobody has been blaming mobiles, but you can't deny that rumors are very 'sticky'.BBC writes, "A biological mechanism that could explain the potential effects of mobile phone radiation has not been identified." And that "There has been no substantial change in the number of adult brain tumours since mobile phone usage sharply increased in the mid-1990s, Danish scientists say."
Read the whole article here. No stopping of mobile phones, as it seems to be.
New Chart: Opt-In Email Lists Still Growing, Slowly but Surely
The general trend of people opting-in to email lists
Email received for business purposes is less likely to cause recipients to opt out, making B2B list size more stable. While the majority of B2B and B2C lists are growing slowly, lists intended for consumer marketing are more than six times as likely to experience accelerated growth.
This past year was particularly challenging for business-to-business email marketers, as seismic movements in the economy resulted in job shifts and losses at almost every company. This meant a sharp increase in lost email addresses, and explains the marked difference in trends for B2B. While nearly 20% of B2C mailers report that their list growth is "Very positive," the number for B2B mailers is only 3%, with the missing 17% found in the "Neutral" category.
Digging deeper, we find that email lists that changed in size during the first half of 2009 grew by an average of nearly 20%. The lists that decreased in size during that period did so by half that rate. In short -- the smaller the organization, the bigger the average rate of increase in list size. Email lists managed by large organizations that decreased in size did so at nearly twice the rate of smaller businesses.
After launching in the 1930s, Rowntree's Chocolate Crisp was originally advertised as "the biggest little meal" and "the best companion to a cup of tea". During the Second World War, Kit Kat was depicted as a valuable wartime foodstuff, with the slogan "what active people need". 'Kitty the Kat' arrived in the late 1940s to emphasize the "rich full cream milk" qualities of the bar and, thanks to contemporary improvements in production methods, also highlighted the new and improved 'snap' by responding to a biscuit being broken off screen. The first Kit Kat poster appeared in 1951, and the first colour TV advert appeared in 1969.

In the meantime, Nestlé UK changed the slogan in 2004 to "Make the most of your break".The new slogan was not embraced outside of the UK and recently Nestlé Rowntree has returned to using the original slogan.
The "classic" American version of the "Gimme a Break" Kit Kat jingle (in use in the US since 1986) was written by Ken Shuldman (lyrics) and Micheal A. Level (music) for the DDB Advertising Agency. Versions of the original have been covered by Carrie Underwood, Shawn Colvin, and many studio singers as well as people who have appeared on-camera in the commercials. The jingle was cited in a study by University of Cincinnati researcher James A. Kellaris as one of the top ten "earworms" - bits of melody that become stuck in your head. Another version of the advertising jingle 'Gimme a break' created for Kit Kat "Factory" commercial in the USA was an original recording by Andrew W.K. W.K. was hired to write a new musical version for their "Gimme a break" slogan. Variations on the Andrew W.K. advertisement included executive dance routines in corporate offices, and a network news room. However, the "classic" song has also been used again since the newer version first aired in 2004.
A 1989 advertisement for Kit Kat, in which a giant panda in a zoo "takes a break" came 30th in channel 4s "100 Greatest Adverts" poll in 2000. Another memorable 1980s UK TV advert for Kit Kat featured a music mogul auditioning a new band, ending with the line "You can't sing, you can't play, you look awful" (Pause) "You'll go a long way."
KitKash is one of the most recent Kit Kat promotions by Nestlé. Premiering in Australia and New Zealand in 2004, each Kit Kat wrapper contained a unique code inside. A winning code was potentially worth $20, $50, $100 or even $10,000. In 2005 the UK's KitKash involved registering an account on the KitKash website and accumulating the codes which each had a point value in order to buy, bid or win products on the site. In 2006 KitKash has been expanded in the UK to include KitKash points in many of Nestlé's other confections as well as spread to Germany (ChocoCash) and France (Kit Kat Kode). USA Kit Kats are also part of the action thanks to Hershey (WrapperCash).
In late 2004, through to the end of 2006, Nestlé Rowntree sponsored New York F.C. As a result the club's home-ground, Bootham Crescent, was renamed to KitKat Crescent.
Free Rotman (PDF) Magazines

Here is a link to at least 11 free Rotman Magazine of Rotman School of Management, Canada:
http://www.asiaing.com/magazine/26.html
This link also includes more than 50 other magazine titles.
But first read Fall 2008's magazine, and the article Too Hot to Handle (Pg # 28) on conflict resolution that may arise in management team that makes decisions.
http://www.rotman.utoronto.ca/pdf/fall2008.pdf
Thursday, December 3, 2009
Gap Analysis
This will help you to write SMART objectives. Then you simply ask two questions - where are we now? and where do we want to be? The difference between the two is the GAP - this is how you are going to get there. Take a look at the diagram below. The lower line is where you'll be if you do nothing. The upper line is where you want to be.
What is Gap Analysis?
Your next step is to close the gap. Firstly decide whether you view from a strategic or an operational/tactical perspective. If you are writing strategy, you will go on to write tactics - see the lesson on marketing plans. The diagram below uses Ansoff's matrix to bridge the gap using strategies:
Strategic Gap Analysis.
You can close the gap by using tactical approaches. The marketing mix is ideal for this. So effectively, you modify the mix so that you get to where you want to be. That is to say you change price, or promotion to move from where you are today (or in fact any or all of the elements of the marketing mix).
Tactical Gap Analysis.
referance: www.marketingteacher.com/Lessons/lesson_gap_analysis.htm
With interviews few and far between there is no such thing as a "practice" interview. Your interview skills must be perfect the first time and every time you interview. While there is no way to anticipate every question you may be asked, there are some questions that come up on a regular basis that universally give job seekers a tough time. Here are the top five interview questions and suggestions for how to answer them.
1)… "So tell me something about yourself." Here is when you need to have your 30 second elevator speech ready. Spend plenty of time in preparing your answer. You'll want to include your profession, how long you've done it, what areas of expertise you offer and any pertinent technology skills. Keep your "speech" full of key words that will grab your interviewers attention. End your statement with an accomplishment that exemplifies what you can do for them. Write it out and practice it over and over until it comes out smooth and natural.
2)… "Why did you leave your last employer?" This question can be especially challenging if you were let go due to performance issues. Be particularly careful not to say anything negative about your past employer while keeping you answer as brief as possible. Some people tent to over talk when they are nervous, but do not offer more information than is absolutely needed. If you had the boss from hell, or your company had turned into a crazy zoo, avoid sharing that. Instead, put your emphasis on what you are pursuing in your next job, as in greater responsibilities, a larger team, a different industry or more opportunities for career growth.
3)… "What are your strengths and weaknesses?" This is a question you'll want to take care in preparing to answer. Make sure that the strengths you mention are those needed most for the job. Back up your claim with an accomplishment that illustrates your strength.
Answering the "weakness" part of the question often stumps job seekers. None of us wants to admit to weaknesses. Avoid the clichéd answers like, "I'm a workaholic" or "I'm a perfectionist with myself." Every interviewer will see through that. Instead, offer a legitimate weakness—but not one that would put you out of the running for the job. Then provide an explanation of how you have learned to compensate for the weakness so that it never compromises your productivity on the job. Have a success story ready to share that shows you have overcome your weakness.
4)… "Tell me a time when..." This question often causes a candidate brain-freeze reaction. The interviewer wants to know how you have handled difficult work-related situations. Get prepared mentally with lots of success stories where you have solved problems on the job. Take time to categorize the work place challenges where you had the opportunity to step up to the plate with the right solution.
5)… "What salary are you looking for?" With today's level of competition for good jobs, salary is often a screening issue. This question will come up early as a way to eliminate candidates above the upper range of the salary range. Avoid stating a specific number. After all, total earnings are usually made up of several factors such as employee benefits, bonuses and commission. It's best to give your answer in a range that provides room for negotiation.
No doubt, you will face one or all of these questions in your next job interview. Give yourself plenty of time to prepare so that you answer them with ease and confidence. Don't get caught without a great answer! The time you spend will be well worth it when you get your next job offer.
You should make every effort to outline who your target market is right up front. There are several questions regarding targeting that you need to answer:
1. Who do you want to attract?
2. What do they need to accomplish?
3. What problems do they need solved?
4. What segment of the marketplace are you interested in attracting?
5. Are you ready, willing and able to provide the solution?
Since the network marketing industry is the focus of this article, this market will be addressed. When segmentation of this market is applied, we see that more than one demographic can be targeted.
posted by Abd ur Rehman
There are different types of marketing strategies based on some criteria. Challenger, Leader and Follower are types of market dominance strategies. Market dominance strategies are used to dominate the market. Cost leadership, Market segmentation and Product differentiation are types of porter generic strategies. Porter generic strategies are built on strategic strength or competing abilities and strategic scope or market penetration. Close followers, late follower and Pioneers are types of innovation strategies. Innovation strategies are meant to trigger the rate of product development and model innovation. It helps the firm to incorporate latest technologies. Intensification, Diversification, Vertical integration and Horizontal integration are types of growth strategies. Growth strategies facilitate the growth of the organization. Marketing warfare strategies are conjunction of marketing strategies and military strategies.
A marketing strategy or a mix of them is chosen only after thorough market research. A marketer should always be ready to face any kind of situations like if the strategy is changed in the middle, he should be able to perform another market research so as to choose the proper strategy, within a short period of time. This can be done easily if you have experience.
posted by Abd ur Rehman
Tips for an effective brochure
Here are some tips on how to print brochures and make them effective enough.
Make a striking cover
The first goal of brochure printing is to get the attention of your viewers. This may not be an easy task. Most people would not have the patience to open every brochure they see. They would only do this if they think the content would be interesting. To get this impression, you must give a lot of thought on your cover. The colors and images you use should match the theme of your brochure. The font and style of the cover should suit the product or service you are selling. The cover must lure your target audience to open it and take the time to read what is inside.
Personalize your message
Now that you have gained the interest of your audience, it is time to talk to them personally. Your writing style should suit your target market. You should use the best language that would effectively communicate to your readers. To win the hearts of your target audience, you must immerse yourself to their lifestyle. If your service is for the youth, then the text that you should use must be light toned and warm. However, for business brochures, the content should be direct to the point and should sound professional. It should be elegant looking, with complete details. Using a unique style in writing for different groups of readers would be an effective way to convince your target audience that your product or service is specifically designed for them.
Know your target market
It is a must to understand and be familiar with your target audience. This would mean that you recognize the needs and wants of your target clients. In addition, knowing these things would help you construct the right message that gives attention to the specific concerns of the readers. This would stir up their interest more, and would work well for your business.
Convince readers to respond
The last part is the most important and most crucial. This is where you convince your readers that the brochure holds information to enlighten them and deserves a try. You must construct your final message such that your audience would be influenced in trying out your service, availing your product, or simply disseminating the information inside.
Be responsible
Bear in mind that you are accountable for the information you have written. Any idea present there would definitely get you back in the future. So before you go on printing brochures, remember to be responsible in imparting a message to lots of people.
Impress your customer with advertising on hold
Consider this - Your client calls you to get some information and you have to place him or her on hold for a few minutes. This is dead time that could be put to better use by using the hold time to tell your customer about new products or services, or steps your company has taken to improve the existing products and services.
Most people do not like to be placed on hold simply because they feel their time is being wasted, but it doesn't have to be that way. If you are taking the time to provide them with information that is directly related to their call anyway, then at the end of the phone call, they won't feel quite so much like they had a lot of wasted time waiting on you to provide the answers that they called for to begin with.
Advertising on hold can be quite an effective tool to get your message out. Imagine a customer calling only for answers and the on hold advertising message just told them about a product or service that they never even knew existed. Now you've leveraged that hold time to your advantage by creating a buyer out of the person seeking information!
You've effectively taken what would otherwise be "dead-time" and turned it into a very powerful marketing tool! The conversion rate when using these advertising on hold messages is phenomenal when used effectively so consider this: If you have to put your customer on hold anyway, wouldn't you rather they hear a message about the latest company innovations, or simply sitting there waiting for you to return for what seems to be a very long time?
Most companies use the advertising on hold system to be sure, and to add a little entertainment to the mixture, short musical snippets can easily be played in between the customer hearing your messages
Unique ways to advertise a product
The following are some ways to promote your business that are a bit unusual and out of the ordinary.
1. Post signs on the stalls in bathrooms.
2. Create coupon flyers and hand them out in heavy traffic places.
3. Place business cards inside books in libraries and bookstores that pertain to the items you are selling or in books about running a business.
4. Create an audio file with your voice and ad and post it on the Internet
5. Create a pod cast promoting your business.
6. Create a video promoting your business.
7. Make wearable signs with poster board and wear them around town.
8. Write your ad on a whole bunch of stickers and put them on your clothes to attract attention.
9. Create a new yahoo group with the subject and theme of your business.
10. Find or create a costume of an item you sell and wear it.
11. Place some drawing bowls in businesses and hold a weekly or monthly drawing for free products
12. Create a free ebook and include your ad.
13. Create free cd software and include your ad.
14. Stop by yard sales and offer to sell your items and donate some of the profit to the homeowners.
15. Offer to teach a workshop on a different subject and give out business cards or other advertising materials at the workshop.
16. Write a song to promote your items and business.
17. Advertise in Spanish speaking newspapers or magazines.
18. If you have the talent you can create useful worksheets or activities in a subject and post them on your website with your ad at the bottom.
19. Ask your local library about selling some of your items in their friends of the library store and donating a portion of the proceeds.
20. Write your ad in chalk on sidewalks.
21. Post up signs for your business at bus stops.
22. Put your ad on the back of some playing cards and sell or give them away.
23. Put door hangers on the doors of businesses and business offices.
